Mail OTP (Email OTP)
Mail OTP is a two-factor authentication method that delivers one-time passwords to users via email. It is an internet-based, cost-effective alternative second-factor authentication solution.
What is Mail OTP?
Mail OTP profiles send users a 6-digit one-time password via email, providing a simple and accessible second-factor authentication method. Any user with email access can authenticate using Mail OTP.
Mail OTP Authentication Method
Configuration Components
Mail OTP configuration consists of 3 main components:
1. Mail Servers
SMTP server configurations used to send email messages.
Configuration Fields:
- Mail Server Name: A descriptive name for the server
- Mail Server IP/Hostname: SMTP server address
- Port: SMTP port number (typically 25, 465, 587)
- Encryption: SSL/TLS settings
- Authentication: SMTP username and password
- From Address: Sender email address
- From Name: Sender display name
Supported Features:
- SMTP authentication
- SSL/TLS encryption
- Multiple mail server support
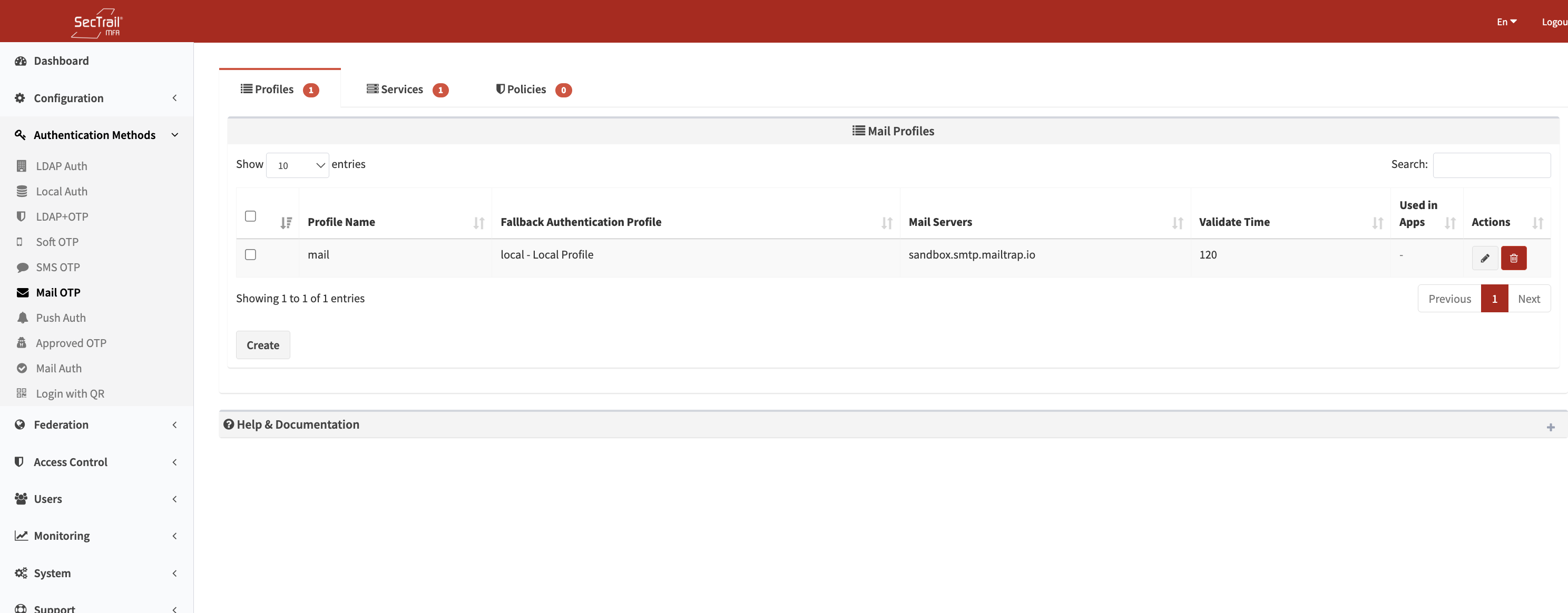
2. Mail Profiles
Defines how Mail OTP codes will be sent to users.
Profile Configuration Fields:
- Profile Name: A descriptive name for the mail profile
- Fallback Auth Profiles: First-factor authentication profiles (LDAP or Local)
- Used to retrieve the user’s email address
- Mail Servers: The mail server(s) used to send OTP messages
- Multiple servers can be added for failover
- Validate Time: Duration for which the OTP code remains valid (in minutes)
- Subject: The subject line of the OTP email
3. Mail Policies
Determines which users authenticate with which Mail OTP profile.
Policy Configuration Fields:
- Mail Profile: The mail profile to be applied
- Authentication Profile: LDAP/Local profile used to retrieve user attributes
- Must match one of the fallback profiles defined in the mail profile
- Retrieves the user’s email address
- Attribute: User attribute to match
- For LDAP:
memberOf,department,title,mail, etc. - For Local:
username,group_name,email,mobile, etc.
- For LDAP:
- Attribute Value: Value(s) to match
- Select from dropdown or enter manually
- Supports wildcard (*) and regex patterns
User Authentication Flow
- User Login: User logs in with username and password (fallback authentication)
- Email Lookup: The system retrieves the user’s email address from LDAP/Local profile
- Email Delivery: The system sends a 6-digit OTP code via the configured mail server
- Code Entry: The user enters the OTP code received via email
- Verification: The system verifies the OTP (within the configured validate time)
- Access Control: If the code is correct, access is granted
- LDAP Users: Must have a valid
mailattribute in LDAP - Local Users: Must have a valid email address in the local user record
- Format: Standard email format (user@domain.com)
Policy Behavior
- No Policy: All users are routed to the default Mail OTP profile
- With Policies: Only users matching the policy rule authenticate with that profile
- Priority: Policies are evaluated top to bottom; the first matching policy is applied
Use Cases
Scenario 1: SMS Alternative
To reduce SMS costs or for users who don’t have SMS access.
Scenario 2: Office Environments
Ideal for users who already work with email open throughout the day.
Scenario 3: International Users
Useful for global users where SMS reliability or cost may vary.
Setup Steps
- Gather SMTP Information: Obtain corporate SMTP server details
- Create Mail Server: Configure the SMTP server settings
- Send Test Email: Use the “Test Mail” button to verify the server
- Prepare Fallback Profile: Create an LDAP or Local authentication profile
- Create Mail Profile: Add mail servers and fallback profiles
- Create Policies: Route users to appropriate mail profiles
- Verify Email Addresses: Ensure all users have valid email addresses
- Application Integration: Attach the mail profile to application profiles
Advantages
- ✅ Cost-Effective: No SMS cost
- ✅ Universal Access: Anyone with email can use it
- ✅ HTML Support: Visually rich OTP emails
- ✅ Multiple SMTP Servers: Failover support
Important Considerations
- Email delivery may be slower than SMS (5–60 seconds)
- Risk of emails landing in spam (SPF, DKIM, DMARC recommended)
- Email addresses must be valid and up to date
- SMTP security and spam filtering must be configured
- Validate time should not be too long (recommended: 10–15 minutes)
Technical Details
- OTP Length: 6-digit numeric code
- Default Validity: 10 minutes (configurable)
- Email Format: Supports HTML and plain text
- Encoding: UTF-8 (including Turkish characters)
- Rate Limiting: Automatically prevents spam behavior
- Retry Mechanism: Uses multiple mail servers for failover