Time-Based Policies
Time-based policies allow you to control when users can access the system by defining allowed days and time intervals. This feature is useful for restricting access outside business hours or assigning different access windows to specific user groups.
What Are Time-Based Policies?
Time-based access control enables administrators to define which users or groups can authenticate during specific days and hours. Policies work at the authentication profile level and are evaluated according to their priority.
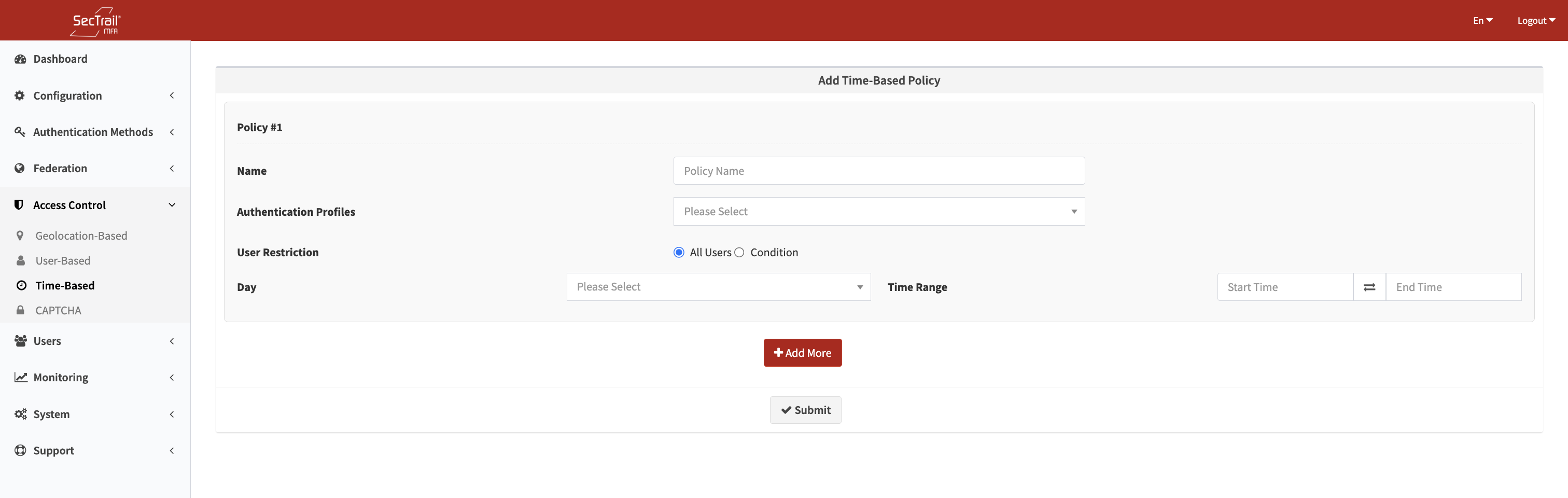
Time Based Policies
Configuration Options
Policy Name
A descriptive name for the policy. This name is displayed in the policy list and logs.
Authentication Profile
Specifies which authentication profile the policy applies to (LDAP, Local, etc.).
Important: The selected profile is used to fetch user attributes.
Attributes and Attribute Values
Define which users the policy applies to.
For LDAP Users:
memberOf— Active Directory groupdepartment— Department nametitle— Job titlemail— Email address- Wildcard (
*) — All users
For Local Users:
username— Local usernamegroup_name— Local group- Wildcard (
*) — All users
Day Selection
Choose the days during which the policy is active.
Options:
- Monday–Sunday (multi-select)
Time Range
Defines the allowed access hours.
Format: HH:MM - HH:MM (e.g., 09:00 - 18:00)
Note: The time range is evaluated using the timezone of the SecTrail MFA server.
Priority
Determines evaluation order when multiple policies exist.
- Smaller number = higher priority
- Priority 1 is evaluated first
How It Works
- User Initiates Authentication
- Policy Evaluation Begins (from highest priority)
- User Attribute Matching:
The system checks if the user matches the policy criteria. - Time Validation:
- If current day & time fall within the allowed range → Access Granted
- Otherwise → Access Denied
- The first matching policy is applied.
Use Cases
Scenario 1: Business Hours Restriction
Goal: IT department should only access the system on weekdays, between 09:00–18:00.
Configuration:
- Days: Monday–Friday
- Time: 09:00–18:00
- Attribute:
memberOf = CN=IT Department,OU=Groups,DC=example,DC=com
Result: IT users can authenticate only during business hours.
Scenario 2: Shift-Based Access
Goal: A manufacturing facility uses 3 shifts; each shift can access only during assigned hours.
Configuration:
- Shift 1: 08:00–16:00 →
department = Production-Shift1 - Shift 2: 16:00–00:00 →
department = Production-Shift2 - Shift 3: 00:00–08:00 →
department = Production-Shift3
Result: Users authenticate only during their shift.
Scenario 3: Weekend Restriction
Goal: Accounting department should not access the system on weekends.
Configuration:
- Days: Saturday, Sunday
- Time: 00:00–23:59
- Attribute:
department = Accounting - Action: Deny (blacklist approach)
Note: A separate weekday allow-policy should be created.
Scenario 4: Emergency / Admin 24/7 Access
Goal: System administrators must always have access.
Configuration:
- Days: All
- Time: 00:00–23:59
- Attribute:
memberOf = CN=System Admins,OU=Groups,DC=example,DC=com - Priority:
1
Result: Admins can authenticate 24/7.
Best Practices
Carefully Plan Priority Order
Policies are evaluated top to bottom based on priority.
Example:
- System Admins – Always Allowed
- IT Department – Weekdays
- All Users (*) – Default business hours
Use Wildcards Wisely
Wildcard (*) applies to all users.
Always place such policies at the lowest priority.
Timezone Awareness
- Time is evaluated according to the server’s timezone
- Consider timezone differences for multiple locations
Avoid Policy Conflicts
Do not create overlapping time ranges for the same user group.
Only the first matched policy will apply.
Provide Emergency Access
Always configure at least one 24/7 policy for administrators.
Setup Steps
- Create or validate the Authentication Profile
- Navigate to Access Control > Time-Based Policies
- Create a new policy
- Define user attributes
- Select days and time range
- Set priority
- Test with different users and times
Benefits
- ✅ Restrict access outside working hours
- ✅ Improve security by reducing attack surface
- ✅ Enforce organizational access policies
- ✅ Flexible per-user/per-group configuration
- ✅ Priority-based evaluation for complex scenarios
- ✅ Detailed logs for denied attempts
Technical Details
- Timezone: Server timezone used for evaluation
- Format: 24-hour time format
- Precision: Minute-level granularity
- Priority: Lower number = higher priority
- Wildcard: Allowed via
* - Logging: All denied attempts are logged
Important Notes
- Verify the server timezone (
timedatectl) - Ensure NTP is running to maintain accurate time
- Consider Daylight Saving Time (DST)
- Avoid locking yourself out during testing
- Wildcard policies should always be last
- Policy updates apply instantly (no restart needed)
Example Priority Ordering
Priority 1: System Administrators → 24/7 Access
Priority 2: Network Team → 24/7 Access
Priority 3: IT Department → Mon–Fri, 07:00–20:00
Priority 4: HR Department → Mon–Fri, 09:00–18:00
Priority 5: Accounting Department → Mon–Fri, 08:30–17:30
Priority 6: All Users (*) → Mon–Fri, 09:00–18:00
Troubleshooting
User Cannot Log In During Allowed Hours
- Verify server timezone
- Ensure attribute values match the user
- Check if a higher priority policy is overriding access
- Review SecTrail MFA logs
Policy Not Being Applied
- Confirm correct authentication profile
- Validate attribute values
- Review policy priority
- Confirm the policy is active
Timezone Issues
- Check timezone via
timedatectl - Ensure NTP is active
- Consider DST changes